Anyone tracing the roots of 2-Propanol, 1-Butoxy-—found in chemical catalogs as Butoxypropanol or Butoxyisopropanol—might spot its rise alongside modern industrial chemistry. Scientists in the early 20th century experimented with etherifying alcohols to stretch their applications beyond household solvents. As factories in Europe and America scaled up demand for specialty glycol ethers, this blend of propanol and butoxy groups started showing up in manufacturing floors and research benches everywhere. Over time, the hands-on chemistry community realized its sweet spot in cleaning, coatings, and as a gentle but persistent solvent. The real shift kicked in when regulatory agencies started looking for alternatives to more toxic compounds used in similar roles. Suddenly, 2-Propanol, 1-Butoxy- stood out as a flexible workhorse not only for paint strippers and cleaning agents but also for those searching safer, effective intermediates.
This chemical belongs, by structure and character, to the family of glycol ethers. The story here is less about fancy molecules and more about everyday usefulness. Companies have packaged it as a clear, colorless liquid, stored in barrels marked with CAS number 5131-66-8. Its approachable volatility, balanced solvency, and relatively low toxicity make it a staple in janitorial supply rooms, laboratories, and paint shops. The product earns trust for its role in thinning water-based coatings and cleaning industrial surfaces without leaving behind oily spots. Anyone bothered by the harshness of methylene chloride or the odor of butyl cellosolve has run into this substance and walked away impressed by the milder nature on both people and surfaces.
The character of 2-Propanol, 1-Butoxy- comes from its blend of hydrocarbon flexibility and alcohol activity. It boils at around 171°C, and the flashpoint sits near 68°C—so it moves into vapor slowly, avoiding immediate fire risk, but asks for sensible storage away from flames. Its density sits below water, which lets it float if spilled on wet floors. The odor is faint, somewhere between sweet and alcoholic, and it dissolves without fuss into water and most organic solvents. Ironically, the chemical’s low surface tension, which frustrates containment, is the very reason behind its effectiveness in cleaning grimy machine parts and stubborn dirt clinging to shop windows.
Chemical drums arrive stamped with precise specs—purity usually over 98%, ester and acid content tightly monitored. In practice, manufacturers provide a Certificate of Analysis showing color, density, and water content measured down to decimal points. Labeling standards stretch beyond the bare formula. The GHS label posts hazard symbols and warnings for eye and skin irritation. European suppliers mark REACH compliance for import-export clarity, while U.S. suppliers make sure OSHA and DOT rules get proper mention. Anyone handling or shipping this solvent appreciates reading the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for instructions tailored to real accidents and exposures, not just dry regulatory recitations. From my own moments coordinating shipments, clarity here saves headaches at customs and avoids rejections on delivery docks.
Production focuses on the etherification of 2-propanol with butanol. Reactors mix the alcohols under acid catalysis, and water gets removed to shift the balance toward the desired ether. Large-scale plants invest in fractionation towers to purify the product from leftovers and byproducts—typically under pressures that speed up the reaction but keep temperatures just below decomposition thresholds. I’ve seen how the quality of the starting alcohols matters; a bad batch leads to stubborn impurities that resist cleanup later. As more companies push for “green chemistry," newer processes swap out harsh acids for recyclable, solid catalysts and lean on closed-loop systems to keep releases low and efficiency up.
This solvent holds up under most normal conditions, resisting attack from acids and bases. Yet, it's not bulletproof. High temperatures can split the ether bond, leading to flammable alcohols. Oxidizers may provoke runaway reactions, a trait that’s made safety managers build added protection into any plant that keeps tanks of this chemical on hand. In laboratory use, its low reactivity pairs well with sensitive processes where other solvents would interfere. Some researchers in polymer chemistry tweak this ether group to form new esters or make it a stepping stone toward complex surfactants. Building on its backbone, chemical engineers create tailored molecules for everything from slow-evaporating paint thinners to specialty resins used in optoelectronics.
2-Propanol, 1-Butoxy- hides behind a crowd of names, tripping up newcomers who scan product lists. Whether listed as Propanol, 1-butoxy-, 1-Butoxy-2-propanol, or even Glycol Ether PB, the molecule remains the same. European documents favor “Butoxypropanol,” while U.S. suppliers sometimes abbreviate it as BPnP. Safety audits and chemical inventory updates require staff to check the full list—nobody likes chasing a missing drum because two names described the same barrel. Commercial cleaners and paint manufacturers brand it under house labels, but always back up claims with the CAS number for a reality check.
No chemical, no matter how gentle its smell or how mild on the skin, earns a free pass on safety. Prolonged contact can irritate skin, and fumes could sting eyes or lead to headaches in a stuffy workspace. Workers rely on gloves, goggles, and good ventilation. Fire codes call for grounded containers, away from sparks: even slow-evaporating solvents eventually reach explosive levels in closed rooms. As I learned during facility walkthroughs, forgetfulness about proper storage often triggers expensive fines and the rare but serious workplace emergency. Clear pick-up in case of spills and anchor storage in cool, shaded locales—two practices that prove their worth during summer heat waves when solvents threaten to bubble over.
Shop floors keep this solvent close for cleaning stubborn grease, prepping surfaces, and as a water-compatible thinner in paints and coatings. Clients in automotive and furniture manufacturing shoot it through sprayers, relying on its steadiness to avoid streaks. Janitorial crews count on it for cleaning glass, metal, and ceramic without streaks or damage. Labs stock it for medium-polarity extractions and as a reactant feedstock. In textiles, it helps with dye transfer by gently shifting polarities; electronics firms have tried it in specialty fluxes. Given its relatively low toxicity compared to alternatives, safety and hygiene teams look favorably on swapping out nastier compounds in favor of this option—even if cost and performance still drive most final call decisions.
Development teams eyed this ether for improved water solubility without totally sacrificing hydrocarbon performance. New blends aim at reducing evaporation rates for coatings, letting paints “level out” before skinning over. Recent R&D efforts chase even safer substitutes but notice that performance often comes at the price of expense or reduced shelf life. By tweaking catalyst beds and reactor setup, some makers deliver higher-purity grades tailored for electronics and medical uses—although adoption rates linger as strict standards require years of validation. At every trade show or industry conference, suppliers gather real user feedback, using those stories to guide tweaks in formulation or packaging for easier handling and reduced waste.
Toxicologists ran trials on lab rodents and cell cultures to measure ingestion, inhalation, and skin absorption risks. Oral LD50 sits above many commonly-used solvents, meaning it takes a hefty dose to prove lethal. Eyes and mucous membranes can show irritation after modest vapor exposure, but routine contact at workplace concentrations rarely passes safety thresholds if proper PPE stays in use. Research points to breakdown via normal hepatic routes, with no evidence of long-term build-up. That’s prompted regulatory agencies to clear its use above the levels imposed on older glycol ethers, though monitoring continues as research explores subtle impacts stemming from chronic, low-level exposures—a hot topic as workplaces tighten limits based not just on acute harm but subtle, cumulative exposure. From my role in workplace health training, convincing crew leads to take even “mild” solvents seriously keeps operations from lurching into complacency—and helps avoid long medical investigations after a minor mishap.
The outlook for 2-Propanol, 1-Butoxy- evolves alongside tightening environmental rules and the relentless search for safer, more effective solvents. Demands for VOC reduction, rising from environmental agencies, push formulators to cut total solvent loads—which throws down a challenge and opens doors for molecules with moderate evaporation yet strong solvency power. As green chemistry picks up steam, some innovators look at renewable feedstocks not only to score environmental points but also to buffer against oil price swings. Broader digitalization and automation in plant management could help dial in purity and cut waste, winning favor in industries where trace impurities spell disaster. With consumer-facing brands angling to label products as safer and “greener,” those guiding research dollars may keep coming back to this workhorse as a proven backbone molecule—worth upgrading but not so easily replaced. In the chemistry world, reliability paves the way for innovation, and 2-Propanol, 1-Butoxy- still has miles left to run.
Most folks probably haven’t heard of 2-Propanol, 1-Butoxy-, but chances are a bottle of cleaning product at home quietly puts this chemical to work. The world knows it by a simpler name too—Butoxypropanol. It carries a long IUPAC title, but what it really does is pretty straightforward: it helps things mix better, cleans better, and slips into a lot of jobs behind the scenes. I remember reading a label and tripping over all those chemical names, only to find out they do some heavy lifting for ordinary chores.
In the cleaning aisle, you’ll see floor strippers, degreasers, glass wipes, and even some laundry detergents containing Butoxypropanol. Companies love throwing it into products for kitchens, bathrooms, and even school hallways. I’ve scrubbed my fair share of grimy tile, and products with this chemical seem to power through stains that plain old soap and water won’t touch. They dissolve grease, ink, and sticky messes with less elbow grease, and that’s worth something when you’re trying to save time and effort.
Factories and paint shops go through barrels of Butoxypropanol. Painters appreciate how it helps paint spread evenly and dry smooth without odd streaks. In textiles, it can break down oils and dirt so fabric comes out fresh from industrial wash cycles. I had a stint packaging industrial cleaners, and folks on the warehouse floor always talked about how much easier cleaning becomes with these chemical helpers.
Whenever you hear chemicals, folks worry about health and safety. That concern’s fair. Short term, it can bother your eyes or skin, like a lot of strong cleaners. If you breathe it in for too long in a closed room, it feels rough on the throat and nose. Over time, heavy exposure leads to bigger risks, so people working with Butoxypropanol need gloves and proper ventilation. I always cracked a window cleaning with anything labeled “use in well-ventilated area.” At work, safety sheets spelled out exactly what steps to take if a spill went sideways.
We want products that clean well without leaving a bigger mess behind. Butoxypropanol breaks down faster than some older solvents, so you don’t get as much long-term pollution. Still, dumping it straight down the drain daily doesn’t seem wise. Growing up near a creek, talk of runoff and chemicals always came up whenever the water changed color after a rainstorm. Manufacturers focus more on safer alternatives, but there’s a balancing act between cleaning power and environmental burden.
Some companies now cut back on harsh solvents and test safer substitutes. There’s been talk about even greener solvents from plant-based sources. As a consumer, it pays to read product tags, ask questions, and pick options designed to do less harm when possible. At work or at home, it’s worth pushing for better training, scrupulous safety standards, and recycling programs so leftover chemicals don’t wind up in landfills or rivers. Change starts small—switching brands, sharing info, or supporting businesses that care about both results and impact.
2-Propanol, 1-Butoxy- sees action in places hidden and obvious, from your kitchen counter to a factory floor. The way it helps shift stubborn messes is impressive, but using it comes with responsibilities. We can’t scrub safety out of the picture, and we can’t toss environmental concerns aside. With a bit more awareness, the choices we make—at work and at home—shape the kind of world we leave behind.
Working with chemicals like 2-Propanol, 1-Butoxy- throws a harsh spotlight on habits at the workbench. I’ve spent years in research labs and every smooth day depended on respecting what these liquids can do. The stuff evaporates fast, gives off sharp fumes, and sets off alarms for both skin and fire safety. This isn’t something to shrug off—ignorance invites trouble. Skin absorbs these solvents, so contact leads to rough hands, red rash, and sometimes deeper health problems. Fumes drift easily; ignoring ventilation risks headaches or worse.
Gloves pull a lot of weight where solvents move around. Nitrile gives a good barrier here; latex tears up and doesn't hold up either. Always check that the glove material stands up to the chemicals in use. Even after the last drop is wiped up, I’d still keep gloves on until everything is scrubbed down. Safety goggles block off another key vulnerability. Just a splash can cause burning or even permanent vision loss—there’s no sense bluffing your way through. At times, I saw colleagues skip goggles because “just a little” seemed safe, but injuries pile up from shortcuts.
Working in a closed room brings risk close. I remember an afternoon in a windowless storeroom; one open bottle was enough to start burning nostrils. Fume hoods and open windows bring tangible relief. It turns out these gases aren’t just a nuisance: with a bit of static, 2-Propanol, 1-Butoxy- jumps to a flash point, and a spark or pilot light can trigger a fire. Flammable liquids like this demand that hot plates, flames, even mobile phones stay put out of reach.
Spills are not rare events. All it takes is a knock of the elbow or a distracted step. The right response hinges on preparation. I always keep absorbent pads and neutralizing agents right by the benches, not tucked away in some cabinet. After wiping up a spill, don’t just toss waste in a normal trash can; these rags become fire hazards themselves. I saw a supervisor almost spark a fire by dropping soaked towels into a standard bin. Special solvent waste containers with tight lids exist for a reason. Treat them as vital.
Clear labels speak louder than any memory or guesswork. Misplaced confidence has no place around solvents. I double-check dates and warning signs before opening anything. Chemical cabinets made of metal with grounded shelves add a real layer of safety; they push fire risk a few steps further from reality. Storing unrelated chemicals together can kick up trouble— don’t store acids next to solvents, since one broken bottle can escalate into a dangerous cloud or worse.
Just because immediate effects seem mild doesn’t mean all’s well. Long-term exposure to compounds like 2-Propanol, 1-Butoxy- has links to lung and liver stress, headaches, and sometimes heavier chronic issues. Companies and labs need regular training, not just for looks, but because memory fades and safety standards drift if left unchecked. Posters, weekly check-ins, and properly enforced rules anchor safe conduct well beyond orientation day.
Too often, comfort with familiarity breeds carelessness. In my own experience, vigilance built into daily routine prevented accidents, not blind luck. The fewer shortcuts, the fewer injuries. Real heroes in chemical handling aren’t the risk-takers but the folks who read the safety sheet, suit up right, and respect the bottle even when they’re in a rush.
Anyone who works with 2-Propanol, 1-Butoxy—sometimes known around the lab as butoxypropanol—picks up pretty quickly that its hazards don’t just lie in the lab itself. One spill across an open shelf, a bit of heat from a sunny window, and you have an accident waiting to happen. These solvents get used everywhere from coatings to cleaning products, but keeping them safe off the production line takes real attention. Flammable liquids like this have a knack for finding trouble when corners get cut.
Direct sunlight heats up containers far more than most folks expect. I’ve seen drums grow warm just from sitting near a south-facing window for too many hours. It might sound picky, but once that temperature climbs, vapor pressure rises fast. Add a spark, or a carelessly tossed rag, and ordinary storage becomes a recipe for a fire emergency. Cool, shaded storage areas don’t just help make insurance companies happy—they save time and money lost to accidents.
The flash point for 2-Propanol, 1-Butoxy sits low enough that leaving any container near a furnace, a bank of hot equipment, or a welding bench quickly ups the odds of disaster. Practical rules look simple enough on paper—store away from heat and sources of ignition—but they matter far more in old buildings, break rooms, and small shops that always seem to stay a bit too warm.
Loose lids and seals give away more product than people realize and mean flammable fumes float into the air. I once worked at a place that swapped old-style drums for newer, screw-top containers; the drop in lingering smell was obvious. Good seals stop evaporation, keep fumes down, and protect everyone’s lungs. For everyday workers, the improvement feels like no more headaches halfway through the shift. Ventilation helps of course, but relying on open windows as a primary defense feels risky during winter or allergy season, when doors stay shut and fresh air drops fast.
Secondary containment sometimes gets ignored. After cleaning up more than one sticky, slick spill, I wish every storage shelf came with a built-in catch tray. These trays or even just deep plastic tubs underneath the original drum keep a single bad pour from spreading. Nobody enjoys the paperwork that follows a half-liter splashing onto a concrete floor.
Hazard labeling seems obvious, but over time tags fade or peel. I’ve relied on color-coded tape and clear labels to dodge confusion, especially when a work area cycles through different chemicals year-round. A quick scan of a storage area can signal if something’s off, like mismatched labels or broken seals.
Fixing poor storage starts with good training and repetition. Safety reminders sometimes feel dull until a near-miss wakes up the room. More workplaces should rotate in hands-on demos for younger staff or those moving over from other areas. For companies looking at cost, spending a bit more on proper storage lockers and spark-proof refrigeration pays back in avoided injuries and downtime.
Regulators and industry groups offer clear ideas on best practices, but personally, peer-to-peer conversations and seeing real-world setups shift far more minds. Walking through a shop with a manager who’s lost equipment to a fire leaves a bigger impression than a memo ever could. For 2-Propanol, 1-Butoxy, the best solutions show up where people stick to habits that protect both products and people.
The name 2-Propanol, 1-butoxy might not ring a bell for most people, but this chemical walks into plenty of factories, cleaning aisles, and labs across the country. It’s a solvent, often useful for dissolving grease, oils, or as a cleaning agent for tough jobs. If you’ve ever scrubbed sticky residue from machinery or polished metal parts, odds are you’ve run across something similar. But familiarity shouldn’t lead to carelessness.
This chemical carries health risks that can’t be brushed aside. Just getting 2-Propanol, 1-butoxy on your skin can cause irritation that takes a while to go away. Workers handling it for hours without good gloves have ended up with red, painful hands. Breathing in its fumes feels just as rough—dizziness, headache, even nausea can hit hard after exposure in a poorly ventilated space. That’s not just stories from manuals. I’ve had co-workers get woozy after cleaning with it in a closed area. They learned quickly that open windows and strong fans make a real difference.
Data from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) show repeated exposure to chemicals like 2-Propanol, 1-butoxy may also hurt the lungs. Breathing issues have cropped up long-term among folks spending years around these vapors. Safety data sheets list this risk plainly, but papers don’t always reach the hands that need them most.
Some shrug off the dangers, thinking strong-smelling chemicals always mean trouble. This one packs a punch, even if it doesn’t burn your nose right away. Spills soak straight through thin gloves. The liquid doesn’t just evaporate—it hangs around and sneaks into the bloodstream after soaking through the skin. The risk escalates for workers who use it day in and day out, not just for people reading labels in a store.
2-Propanol, 1-butoxy has found its way into degreasers, ink removers, and even some cleaners in offices. Office staff sometimes grab industrial sprays or wipes, not realizing these weren’t made for casual touch. At home, that mix-up happens too. “If it cuts grease at work, we’ll use it in the garage,” I’ve heard people say. That logic comes with risk—a dab on a rag is enough for fumes to build up fast in small spaces.
Classified as hazardous under OSHA and EU guidelines, this chemical’s risk is no secret. Acute overexposure can lead to nervous system effects, while long-term skin contact can leave lasting damage. It’s no stretch to say a job that skips proper gear is asking for trouble.
There’s no magic fix, but smarter habits cut the danger sharply. Employers need to hand out gloves that resist solvents, not the thin ones that give up at the first splash. Training should put the risks front and center—not buried in fine print. If proper ventilation feels like overkill, it helps to remember one story of someone getting sick just from hurrying through cleanup in a stuffy corner.
For the curious home tinkerer, skip the temptation to borrow strong shop chemicals for household chores. Stick to safer stuff for home jobs, and always lock up cleaning agents away from kids and pets. Labels should get the same respect you’d give to any sharp tool—learn before you use, not after you’re in trouble.
Folks who spend their days around chemicals like 2-Propanol, 1-butoxy know shortcuts add up. Calling out hazards, sharing real-life stories at safety meetings, and swapping advice about better gloves and ventilation have a bigger impact than signs on a wall. Staying safe isn’t about paranoia—it’s about treating risky substances with the respect every worker and family deserves.
2-Propanol, 1-Butoxy-, better known in some chemical circles as butoxypropanol, shows up in more workplace settings than you might expect. Its main calling card has always been as a solvent, mostly because of how well it blends with water and other organic liquids. You can catch its scent in everything from industrial plant floors to craft supply shelves.
Industrial cleaning has always been a job for strong, reliable chemicals. Companies often lean on 2-Propanol, 1-Butoxy- to bust through oily residues, grease, and ink. Its structure gives it the muscle to dissolve gunk that water can't touch. If you’ve ever used a heavy-duty floor stripper or checked the label on a multipurpose industrial cleaner, there’s a fair chance you've used something that owes its power to this solvent.
In auto shops and machinery plants, workers trust this chemical to prep metal surfaces or degrease tricky engine parts. By helping cut down scrubbing, it saves time and lowers injury risk, which anyone who's ever scrubbed machinery by hand can appreciate. It does the heavy lifting where soap and water fall flat.
Walk into a paint store these days, and you’ll see rows of cans promising smooth application and long-lasting finish. 2-Propanol, 1-Butoxy- helps paints spread evenly and dry without streaks. Paint producers use it to deliver that promising finish, especially for water-based varieties where it balances evaporation. Even the ink on your paperback novels or food labels likely dried faster and sharper because this solvent sped up the process on the press.
The world of coatings and varnishes also benefits. Manufacturers rely on butoxypropanol for its ability to reduce viscosity, making their products easier to apply by brush or spray. This makes it a quiet enabler in industries where every second counts, like construction sites and print shops hustling to meet deadlines.
The chemical isn’t limited to industrial use. Look into fragrances, lotions, and some hair dyes—there it is, helping dissolve perfume oils and other ingredients. In household air fresheners and specialty soaps, it balances the solution and helps fragrances linger in the air or on your hands.
Some cosmetics manufacturers list it as a carrier solvent, pulling scent and active ingredients into a smooth, usable form. In these roles, it quietly supports a better, more consistent experience for the end user. I’ve seen firsthand how product labs struggle with formulas that separate or apply unevenly, and this chemical saves hours of headaches.
What gets tricky is protecting workers and the environment. Strong solvents can irritate skin and lungs, especially with daily exposure. Shops and factories have shifted toward better ventilation and personal protective equipment. Regulations require smarter chemical management to cut down on spills and reduce polluting runoff, especially since solvents can affect waterways.
As green chemistry gains traction, some companies are investigating lower-toxicity alternatives. Still, for now, few options match butoxypropanol’s blend of power and flexibility. The push continues for improved labeling, safer storage, and clear worker instructions, all aimed at reducing hazards without sacrificing performance.
Anyone who's worked in cleaning, painting, or even cosmetics knows a steady hand and the right ingredient can make tough jobs easier. 2-Propanol, 1-Butoxy- finds these roles because, plain and simple, it works where others might fall short—though the need for care and responsibility only grows as we realize how much is at stake.
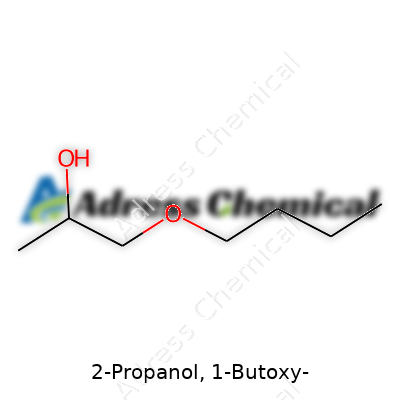
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | 1-Butoxypropan-2-ol |
| Other names |
1-Butoxy-2-propanol Propylene glycol butyl ether Butoxypropanol Propylene glycol monobutyl ether Butoxy-2-propanol |
| Pronunciation | /tuː-ˈprəʊpənɒl wʌn-ˈbjuːtɒksi/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 5131-66-8 |
| Beilstein Reference | 1819439 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:4360 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL16343 |
| ChemSpider | 7621 |
| DrugBank | DB08240 |
| ECHA InfoCard | The ECHA InfoCard for 2-Propanol, 1-Butoxy- is: **03-2119980267-30-0000** |
| EC Number | 203-961-6 |
| Gmelin Reference | 81137 |
| KEGG | C19727 |
| MeSH | D017180 |
| PubChem CID | 12006 |
| RTECS number | UC6475000 |
| UNII | 6K82R1MX0S |
| UN number | UN1993 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C7H16O |
| Molar mass | 132.22 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Alcohol-like odor |
| Density | 0.809 g/mL at 25 °C |
| Solubility in water | Miscible |
| log P | 0.8 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.762 mmHg (at 25 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 16.1 |
| Basicity (pKb) | pKb: 5.06 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -50.4·10⁻⁶ cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.408 |
| Viscosity | 2.89 mPa·s at 25°C |
| Dipole moment | 1.93 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 418.6 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -457.6 kJ/mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) | -4451.0 kJ/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | D08AX08 |
| Hazards | |
| Pictograms | GHS02, GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H226, H315, H319, H336 |
| Precautionary statements | P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P337+P313, P370+P378, P403+P235, P405, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 2-Health, 2-Flammability, 0-Instability |
| Flash point | 52 °C |
| Autoignition temperature | 230 °C |
| Explosive limits | 1.1 - 12.7% |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 Oral rat 6470 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | 1910 mg/kg |
| NIOSH | LW8400000 |
| PEL (Permissible) | 100 ppm (TWA) |
| REL (Recommended) | 50 ppm (230 mg/m3) TWA |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | 200 ppm |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
1-Butanol 2-Propanol Butyl acetate Butoxyethanol Isopropyl alcohol |