2-Methoxy-1-propanol acetate didn’t get much attention in the early days of organic solvent research. Folks in the 1970s dug into ether and ester chemistry to create solvent blends with fewer health hazards—a pretty tall order given industry’s love affair with toluene and xylene. As the environmental standards rose, so did the call for materials with a lower impact on air and health. That’s where this acetate slipped in: born from the push for alternatives that could handle stubborn coatings and inks without raising safety alarms quite as loudly as traditional picks. This compound came about thanks to the trial-and-error approaches of process chemists adapting old esterification strategies to match stricter regulations.
What stands out with 2-methoxy-1-propanol acetate is its marriage of efficiency and versatility. The product belongs squarely to the family of glycol ether acetates, and the reason manufacturers keep it in their toolbox is simple—diluting, cleaning, dissolving, and coupling. The acetate group attached to the methoxypropanol backbone changes its personality from a pure solvent into something more: it can mix with many other ingredients and evaporates just fast enough for speedy operations in coatings plants.
To really get why this solvent finds a home in paint shops and printing facilities, you look at basics first: it exists as a clear, colorless liquid. It carries a faint ether-like smell that you notice long before you suffer irritation. Water solubility doesn’t reach sky-high levels, but enough to be handy for blending. Its boiling point sits around 145°C, helping avoid premature evaporation during processes that involve a bit more heat. The vapor pressure lands lower than an average acetate, meaning it lingers just enough to keep surfaces wet. Flammability isn’t negligible, so anyone near open flames has to take care. Overall, the molecular structure—part ether, part ester—brings out a set of balanced traits that chemists keep coming back for.
Every barrel or drum of this product demands a careful eye on purity, impurity levels, and water content. Purity percentages usually need to hit at least 99% if the customer has high standards for coatings or electronics. Water should stay under 0.1%, given how easily tiny amounts change the way coatings dry or how plastics handle mixing. Labels flag its UN number for transport safety, CAS number for identification (108-65-6 for this compound), and carry warnings required by Globally Harmonized System (GHS) regulations: avoid eyes, avoid flames. Safety Data Sheets don’t just sit in the background—they steer everything from storage room ventilation to disposal.
Making this glycol ether acetate follows a straightforward routine with just a few sharp edges. Typical synthesis brings together 2-methoxy-1-propanol and acetic acid, letting them react under catalytic conditions. Acid catalysts like sulfuric acid, heat, and perhaps a remover like toluene to pull away water created in the reaction keep production humming. After the main reaction finishes, distillation strips off low boilers and the pure product takes its place. Troubles crop up if you ignore purification, since trace acids or byproducts throw a wrench into downstream applications. Chemical engineering teams often tweak these steps to suit different plant scales, but the backbone remains the same.
Once you have this acetate on hand, it opens the door to plenty of further modifications. Hydrolysis flips it back to its alcohol and acid roots, handy when adjustments to solvent profiles seem necessary. Its ester group stands ready for transesterification, letting formulators tailor-make solvents for special needs in adhesives or coatings. It can participate in polymerization reactions where a controlled release of the acetate improves surface finish or influences film formation. Every move in this class of chemistry relies on controlling side reactions, especially when pushing for high yields or cost efficiency.
You’ll hear chemists toss around names like PGMEA (Propylene Glycol Monomethyl Ether Acetate) or 1-Methoxy-2-Propanol Acetate. Global markets throw in their translations and product codes: Dowanol PMA, Arcosolv PMA, and other trademarked versions. Synthetic origins and purity levels sometimes show up in the name—the numbers and letters aren’t just for show, since they reveal which plant or batch produced a particular shipment.
Spending any amount of time around glycol ether acetates builds a respect for their health profile. Direct skin or prolonged inhalation exposures lead to headaches or irritation, even if the compound ranks as less hazardous than older solvents. Plants involved in large-scale use enforce strict ventilation, personal protective gear, and exposure monitoring. The flash point, hanging above 42°C, calls for careful storage in cool and dry spots well away from ignition sources. Fire marshals and occupational safety teams follow protocols from OSHA and REACH, and Europe’s push for safer chemicals keeps driving down allowable exposure limits. I’ve seen operations that didn’t take GHS pictograms seriously deal with expensive corrective actions after inspections.
Coatings, printing inks, electronics, and cleaning solutions—these all depend on 2-methoxy-1-propanol acetate. Paint formulators love it because it keeps pigment dispersed, dries without streaking, and doesn’t yellow finishes. Printing houses splash it into quick-drying ink recipes, counting on its low toxicity profile to keep up with tight safety standards in food-safe packaging. Circuit makers use it to strip photoresists or thin coatings on chips, since it won’t chew up sensitive circuit lines. Cleaning products in factories value its power to dissolve resins and adhesives where water alone fails. Additives in adhesives rely on the compound to spike clarity and flow without wrecking performance.
Research teams at chemical firms keep circling back to this molecule for a reason: its structure offers a platform to build safer, greener solvent systems. Development pushes include tweaking production for more renewable feedstocks or creating blends that outperform classic formulations. Academic labs spend time mapping its reaction kinetics or modeling health impacts, looking for ways to meet regulatory hurdles before new restrictions hit. Researchers now lean into lowering carbon footprints for large-scale synthesis and figuring out recycling streams for used solvents, since regulators and customers alike demand more responsible handling from start to finish.
Toxicity talks swirl around glycol ethers, so real-world testing matters. Studies on this acetate show modest acute toxicity—workers have reported headaches and nausea but not the dire reproductive or chronic effects found with older solvents like ethylene glycol ethers. Rats take much higher exposures before showing issues, and skin absorption falls well below worrying thresholds for regular industrial contact. Chronic studies try to map subtle effects on the liver or testes, since regulators in Europe and the US want hard limits set. Child safety professionals track emissions in home paints or school markers to make sure residues don’t exceed public health recommendations. Industry pushes for transparency, releasing in-depth reports to defend its role outside of “forever chemicals” territory.
Market watchers pin ongoing demand on industries’ stubborn need for solvents that balance evaporation rate, solvency, and safety. Regulatory pressure keeps tightening, so next-gen versions center around higher purity, lower toxicity, and easier recycling. Companies keep funding projects focused on biobased and circular production routes—no one wants solvents dependent on fossil origin forever. In electronics, the push for smaller, more sensitive devices requires even tighter control of solvent residues, so new grades of the compound get tailored for traceability and purity. I expect automation in production and tracking safety in real time to take bigger roles soon, since reducing human error means fewer expensive recalls or workplace accidents. Supply chains now rank traceability as a must, not a nice-to-have, so tracking batches from factory to end user becomes more important year after year.
Walking through a hardware store, the aisles stacked with cans of paint and buckets of coatings, most people overlook the alphabet soup of ingredients on the labels. One of those unassuming names, 2-methoxy-1-propanol acetate, shows up far more than most realize. This isn’t some shadowy chemical with a single job—it’s a workhorse solvent, simple yet crucial. I’ve spent hours sorting out paint splotches, scrubbing my hands after handling coating products, and, like anyone curious about what’s really in those cans, found this stuff does more than just “blend.”
Take any water-based paint or ink. There’s always a delicate balance between flow, drying speed, and that perfect finish. 2-methoxy-1-propanol acetate brings muscle to the table right here. Rather than thinning the product like water does, it carries pigment and resin together, then slips away at the perfect rate as the job dries. That steady evaporation matters. Paint that dries too quick tends to streak or turn brittle, ruining hours of work. Go too slow, and dust or fingerprints ruin the day. This solvent keeps the drying just right, helping everyday paint jobs wind up looking professionally smooth.
Driven by speed, efficiency, and waste control, industrial manufacturing leans on smart ingredient choices. This solvent ends up powering printing presses and coating metal surfaces because it tackles two big headaches: it cuts through greasy fingerprints and mixes well with all sorts of resins and colorants. In inks, its performance defines whether that magazine cover dries crisp or stays tacky. While some older solvents leave behind nasty odors or cause headaches from fumes, this chemical keeps workplace air a touch more bearable. Loading a press with a batch of ink, you quickly notice how some blends just don’t play nice—2-methoxy-1-propanol acetate reduces the drama, offering consistency press operators respect.
Not every useful solvent comes with safety baked in. I hit a wall reading stories about headaches and skin irritation from cleaning up after painting. This solvent, while less intense than some, still calls for respect. Goggles and gloves aren’t just a box-ticking exercise—they make the difference between a simple afternoon and a world of irritation. Manufacturers now aim to keep fumes down, but there’s more work to do. Regulations in places like the EU have already started to rein in careless use, forcing safer factory practices. The push to produce less-hazardous alternatives isn’t just a green talking point—no one wants solvents building up in groundwater, either.
Choices at the store shelf or in factories have ripple effects upstream. Switching to less impactful solvents takes real investment—new machines, fresh training, and better ventilation systems. Research keeps pushing for greener solvents, building off molecules like this one, but nothing matches a sharp eye for safety and ventilation in the shop or at home. For now, those who use paints or print for a living have reason to care about their solvents, both for the work itself and for what they’re breathing in. Watching for shifts in regulation and keeping safety gear as basic as a mask close at hand will keep the chemical’s benefits outweighing its risks.
Anyone working with chemicals knows every substance asks for its own set of rules. 2-Methoxy-1-Propanol Acetate, sometimes called propylene glycol methyl ether acetate, carries risks nobody wants to ignore. It finds its way into paints, coatings, inks, and cleaners. It creeps into workplace routines, but it demands respect just the same.
Working in rooms with poor ventilation once made me dizzy, headachy—basic signs the fumes weren’t harmless. The vapors from this solvent build up quickly, and people wind up exposed before they know it. Ensure windows stay open, and exhaust fans running. Open doors if possible. Local exhaust systems—those hoods over tables—pull the vapors away right at the source. Cheap paper masks offer zero real protection; fitted respirators with organic vapor cartridges outmatch them every time. I carry mine whenever a label mentions the word “acetate.” It smells sweet, but don’t trust that scent. The real test: If your nose notices it, the room needs much more airflow.
Nobody likes dry, irritated hands, and 2-Methoxy-1-Propanol Acetate dries skin like few others. I learned early not to use cotton gloves—disposable nitrile gloves stand up to this solvent much better. It soaks through latex in minutes. Forget bare hands; skip those flimsy shop rags, too. Lab coats with fitted cuffs and splash-resistant aprons keep accidental spills from running down sleeves or soaking through clothing. Wash up fast with mild soap and cool water if anything hits skin. Scrubbing only rubs the chemical in deeper.
A face shield might look silly until a splash lands near your eye once. I’ve seen too many people squinting and blinking after quick splatters. Wear chemical splash goggles, not safety glasses. Regular glasses can’t cover the gaps. Eyewash stations, close at hand, save eyes—fifteen minutes of rinsing flushes out irritation before it grows dangerous. Don’t replace water with saline. Tap water gives relief in a hurry, and that’s what counts during those panicked first moments.
No chemical belongs in the wrong container. Always use metal or HDPE storage cans with secure lids. I label mine with bold markers, and I don’t trust memory. I’ve seen solvent eat right through thin plastic after just a week. Keep it away from sparks, heat, and sunlight—this stuff easily lights up in the wrong conditions. Spills spread fast on hard floors, so keep clean-up kits nearby: absorbent pads, sand or spill booms work wonders in a pinch. Never pour waste down the sink. Old leftover solvent sits in a sealed drum, waiting for licensed disposal.
Anyone working with chemicals learns from small mistakes and stories shared in break rooms. Training sticks best when it feels real. Read the safety data sheet before opening a new drum. Bring in safety drills so reactions come quicker, not slower, in emergencies. Some shops keep a written checklist taped near their workbench. Simple, visible reminders do more than dull safety posters ever could.
Handling 2-Methoxy-1-Propanol Acetate demands common sense, sturdy gear, and attention to tiny details. The right routines build habits that keep you and those around you out of trouble.
Many folks in laboratories or factories don’t think twice about the storage details of solvents like 2-Methoxy-1-Propanol Acetate. Years ago, during my early days in a paint factory, we didn’t pay enough attention. The labels called for "cool, dry, and well-ventilated" spaces, so we figured any old shelf would do. That nearly cost us a serious mess, since volatile solvents have minds of their own—and their risks only grow when heat and oxygen come into play.
This particular solvent isn’t as flammable as some, but it’s no water. If left in a hot room, vapors build up, and fire risk jumps. I can still picture a coworker laughing about “just a little warmth” being okay. The reality is, a single spark in a warm, enclosed storeroom could send you running. So it makes sense to store this chemical below 30°C, far away from places that catch the sun in the afternoon. Direct heat dries out labels and can warp containers, leading to slow separation or even a leak.
Humidity wreaks havoc on more than paper. Moist air nudges some solvents toward slow breakdown, especially if containers sit open or poorly sealed. I’ve watched new guys reach into bins and grab old bottles with sticky caps and faded warnings; in more than one case, water had found its way in. That contamination changes the substance, and you can forget about predictable results. Keeping everything airtight and dry helps avoid these pitfalls, and it cuts down on waste from ruined stock.
Chemical fumes tend to settle in corners if there’s no fresh air. In paint shops, the folks who cough the most are usually the ones working closest to the shelves. A duct or exhaust fan might seem like overkill, especially in cooler climates. After cleaning up headaches caused by forgotten spills and stale air, I say it’s best to invest. Fumes from 2-Methoxy-1-Propanol Acetate can irritate the lungs and, over time, make a cramped room dangerous, especially when containers are being opened and closed every day.
Plastic cans sound convenient—until you see one buckle under stress or age. Metal drums, with a proper lining, stand up much better. Each label should show hazard symbols and date of arrival. When an accident happens, nobody wants to guess what’s inside or how long it’s been there. I’ve lost count of the near-misses traced back to containers missing that info. Clear labeling means fewer questions in a crisis and makes auditing simpler.
Shelf checks once a week catch leaks early and spot outdated stock. Rotating old supplies to the front and recording every bottle as it’s added keeps surprises at bay. Simple logs stuck to the wall beat digital spreadsheets that nobody ever checks on the shop floor. Give responsibility to the folks using the chemicals the most—they’ll spot if something smells strange or looks off long before an inspector shows up.
It’s easy to slack on chemical storage when the boss isn’t watching. Setting up a routine, sticking to temperature-and-moisture rules, and investing in solid containers and fans ends up saving money and keeping everyone safer. The risk may seem small, but as experience has taught me, ignoring the basics never pays off in the long run.
Questions about chemical safety pop up often, especially for compounds like 2-Methoxy-1-Propanol Acetate that show up in paints, inks, and cleaning agents. Labels might warn about fumes or skin irritation, but people rarely go beyond the surface. As someone who’s handled plenty of solvents, there’s a big gap between technical data sheets and what actually happens in a workshop or lab.
Most containers carry hazard symbols that signal caution but leave out the story behind the risk. The health effects tied to this chemical usually center on vapors. Breathing in even a moderate amount can cause dizziness, headache, and throat irritation. Let’s be real — anyone who’s stripped paint in a tight space knows what that feels like. Eyes and skin get irritated if you splash it, and some folks develop rashes after a day’s work.
Government agencies like the European Chemicals Agency place 2-Methoxy-1-Propanol Acetate under substances that require strong handling rules. They point out risks to the nervous system and potential effects on unborn children at higher exposures. The US Environmental Protection Agency groups it in a basket of solvents called “glycol ethers,” several of which damage red blood cells and can mess with reproduction if used recklessly. Those facts don’t stop auto shops, print shops, or even some home hobbyists from choosing it over safer formulas.
At work, nobody plans to soak their hands in solvent or breathe it day after day — but leaks and poor ventilation make that too common. Respirators sit unused in lockers if they’re uncomfortable or if nobody explains why wearing them matters. I’ve seen shortcuts taken because deadlines or budgets seem more urgent than a risk that feels distant. A headache or sore throat is easy to ignore, but those small symptoms add up. Some people chalk up fatigue or skin complaints to stress or poor sleep, rarely connecting it to the air they’re breathing.
Spills matter more than people admit. Wiping solvent off a bench with bare hands feels faster in the moment, but repeated exposure lets the chemical slip through the skin into the bloodstream. Studies from occupational health clinics have found workers with elevated levels in their urine after years of "just quick cleanups." Even schools get caught out — art rooms favor affordable, strong solvents, without always teaching safe handling until someone gets a nosebleed or nausea after a project.
The big companies have moved toward switching out the more toxic glycol ethers and swapping in alternatives where possible. Air extractors and gloves become more common where managers see the payoff in fewer sick days and regulatory fines. Even for the do-it-yourself crowd, simple steps protect health: crack a window, wear gloves, and never store these liquids in drinking bottles. I once saw someone use a soda bottle for leftover solvent at a community clean-up — not realizing the danger until a child grabbed it by mistake.
Clear labeling, better training, and investment in safer substitutes save trouble down the line. Some places offer water-based versions of products that once required strong solvents; these options give similar results with much lower risk. It does mean changing habits and sometimes spending a little more upfront, but the payoff comes in fewer headaches — both literal and legal.
2-Methoxy-1-Propanol Acetate mostly flies under the radar for folks outside chemical industries, but its impact shows up in more places than most realize. This compound goes by a few names, but in the lab, its chemical formula pops up as C6H12O3. For record-keeping and ingredient lists, its CAS number stands at 70657-70-4. Whether you’re reading a safety sheet at work or double-checking formulas for a project, knowing these details steers you clear of confusion.
I’ve spent enough time in repair shops and paint stores to spot the patterns—chemicals like 2-Methoxy-1-Propanol Acetate help stretch raw materials to meet tough jobs. It’s not a headliner, but paints, inks, and coatings lean on it for more than just mixability. In printing, for example, this compound pulls double duty, carrying color across pages and keeping drying times on target. Nobody wants smudged brochures or sticky product labels. Without helpers like this acetate, smooth production becomes shaky.
In industries where this acetate gets used, safety isn’t just a good idea—it’s the routine. Factory floors, especially those churning out adhesives and cleaning agents, depend on workers recognizing every code and chemical name. One missed step can end with headaches, breathing trouble, or worse. Safety data sheets include the CAS number to stop any guessing game. I’ve seen mistakes from skipped reading or unclear labeling—problems multiply fast. Upfront naming cuts the risk. Clarity pays off when the stakes get high.
Groups concerned about air and water safety often raise the flag on solvents and acetates. I sat in on meetings where neighbors nervously asked about chemical storage and leaks. 2-Methoxy-1-Propanol Acetate isn’t the only one under a microscope, but its formula and CAS number give community watchdogs and environmental scientists a common reference. Tracking spills and emissions turns into real action instead of endless debate. Accurate identification helps watchdogs and regulators spot leaks quickly, stopping bigger problems before they start.
I’ve noticed a powerful effect when industry folks, regulators, and the public all use the same language. That includes knowing both the formula and the CAS number for chemicals like 2-Methoxy-1-Propanol Acetate. In my experience, confusion drops and solutions emerge when everyone’s on the same page, whether you’re labeling barrels, logging shipments, or drafting new rules.
Plenty of safer alternatives and process changes now get explored as more people question longtime practices. Open information—down to the right numbers—means the next generation of coatings, cleaners, and paints can move toward less toxic, more sustainable formulas. Keeping track of chemicals at this level doesn’t just fill out a spreadsheet. It forms the bedrock for safer, more responsible invention across industries.
| Names | |
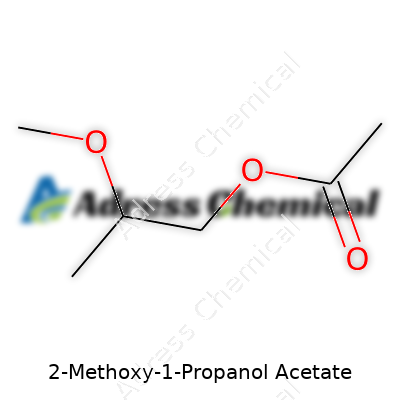
| Preferred IUPAC name | 1-Acetoxy-2-methoxypropane |
| Other names |
Propylene glycol monomethyl ether acetate 1-Methoxy-2-propyl acetate PMA PGMEA Dowanol PMA Propylene glycol methyl ether acetate |
| Pronunciation | /tuː ˈmiːθəkˌsi waɪn ˈprəʊpənɒl əˈsiːteɪt/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 70657-70-4 |
| Beilstein Reference | 1761051 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:88161 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1625598 |
| ChemSpider | 12224 |
| DrugBank | DB14424 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 03ea6017-5e6e-4b9b-8191-fbc78a51f7bf |
| EC Number | 203-603-9 |
| Gmelin Reference | 1301934 |
| KEGG | C19596 |
| MeSH | D058137 |
| PubChem CID | 12232 |
| RTECS number | UU3675000 |
| UNII | 9K5B8F8MY6 |
| UN number | UN3272 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C6H12O3 |
| Molar mass | 132.16 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Mild, fruity |
| Density | 0.966 g/mL at 25 °C |
| Solubility in water | Miscible |
| log P | 0.38 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.43 mmHg (20°C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | pKa ≈ 15.5 |
| Basicity (pKb) | pKb: 10.7 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -49.5·10⁻⁶ cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | nD 1.405 |
| Viscosity | 1.1 mPa·s (25°C) |
| Dipole moment | 2.05 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 360.7 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -589.3 kJ/mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) | -3595.6 kJ/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | D02AE10 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling | GHS02, GHS07 |
| Pictograms | GHS02,GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H226, H319, H336 |
| Precautionary statements | P210, P243, P261, P271, P280, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P337+P313, P403+P233, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 1-2-0 |
| Flash point | 46 °C |
| Autoignition temperature | 345 °C |
| Explosive limits | 1.5–8.0% |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 Oral Rat: 8532 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | 6,500 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| NIOSH | PCW |
| PEL (Permissible) | PEL: 100 ppm (540 mg/m³) |
| REL (Recommended) | REL: 50 ppm (270 mg/m³) |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | IDLH: 1,500 ppm |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Propylene glycol methyl ether Propylene glycol methyl ether acetate Ethylene glycol methyl ether Ethylene glycol methyl ether acetate 1-Methoxy-2-propanol 1-Methoxy-2-propanol acetate |